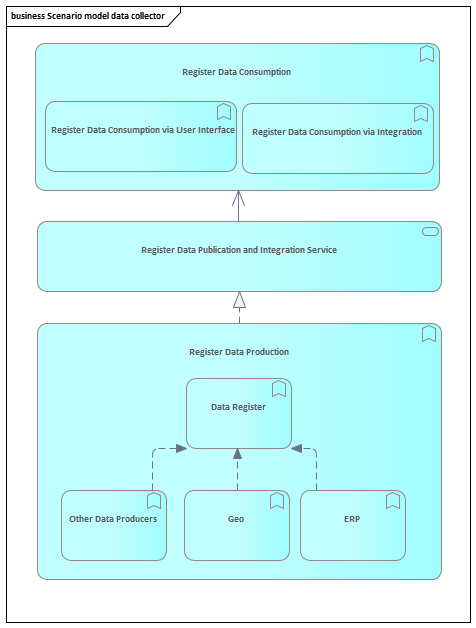
In this scenario data is collected form the various data producing applications and combined and standardized in the master data register. This means that data is modified in one of the data producing applications and eventually enriched in the data register. The data register is mainly a data replication with a standardized data model of the other data producers. An example is a datawarehouse
Advantages
- All data directly integrated at hand.
- Standardization of data is possible within the Data Register
- There is a possibility to enhance data by intelligently combing it to new information.
- High availability only for the data register when consumers need a high availability
- Data validation can be implemented in the system where it is most advantageous/efficient
- Reuse of screens, validations, existing data integrations and workflows
- Supports a iterative migration to a more centralized (register) scenario
Disadvantages
- When integration of data is asynchronous the data is not the same as in source systems on every moment. This will not be a problem if timing is not an issue.
- When synchronization of data is synchronous high availability requirements for the registry systems is necessary
- Data replication and need for extra storage
- Fetching and distributing data back and forth is equally much work as with an MDM solution
- Possible very complex data transformations necessary
| Versie | 1.0 | | Creatie datum | 02-05-2021 |
ERP (or EAM) functionality for the registration of data within a number of highly standardized processes using asset data.
| Auteur | Bert Dingemans |
| Alias | |
| Stereotypes | ApplicationFunction |
| Details van ERP |
Application and database integration like webservices, file transfer, database links, views etc. In a later phase we will model the various integration methods and model these in detail
Abstract architectural entity for the register data consumers, all user interfaces and data integrations are an master data consumer
Logical application function for the storage and transformation of master data in various source function and the data register function
Other MDM data producing application functions like the delivery of office files etc.
Logical services that publish the data from the register to various register data consumers
All kinds of user interfaces in which an user can consume data via a (graphical) user interface. Examples of user interfaces are reports, forms, portals graphs, geoviews etc.
MDM like function that aggregates all the data in a standardized data model
Geo functionality and register in combination with the extraction of asset data in combination with geo data and maps
| Auteur | Bert Dingemans |
| Alias | |
| Stereotypes | ApplicationFunction |
| Details van Geo |